The Voyager 1 spacecraft, launched by NASA on September 5, 1977, is humanity's most distant emissary in space. As it ventures further into interstellar space, its speed continues to captivate scientists and space enthusiasts alike. Understanding the velocity of Voyager 1 not only highlights the technological advancements of its time but also underscores humanity's relentless pursuit of knowledge beyond our solar system.
Voyager 1 has become a symbol of human ingenuity and exploration. Its mission was initially designed to study the outer planets, but it has far exceeded expectations by traveling beyond the heliosphere and into interstellar space. This spacecraft carries with it the hopes and dreams of humanity, symbolizing our desire to explore the unknown.
In this article, we will delve into the details of Voyager 1's speed, its journey through space, and the implications of its discoveries. By examining its velocity and trajectory, we can gain insights into the capabilities of modern space exploration and the potential for future missions.
Read also:Discover The World Of Peppa Pig Characters A Complete Guide
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- How Fast is Voyager 1 Traveling?
- The Journey of Voyager 1
- Technical Details of Voyager 1
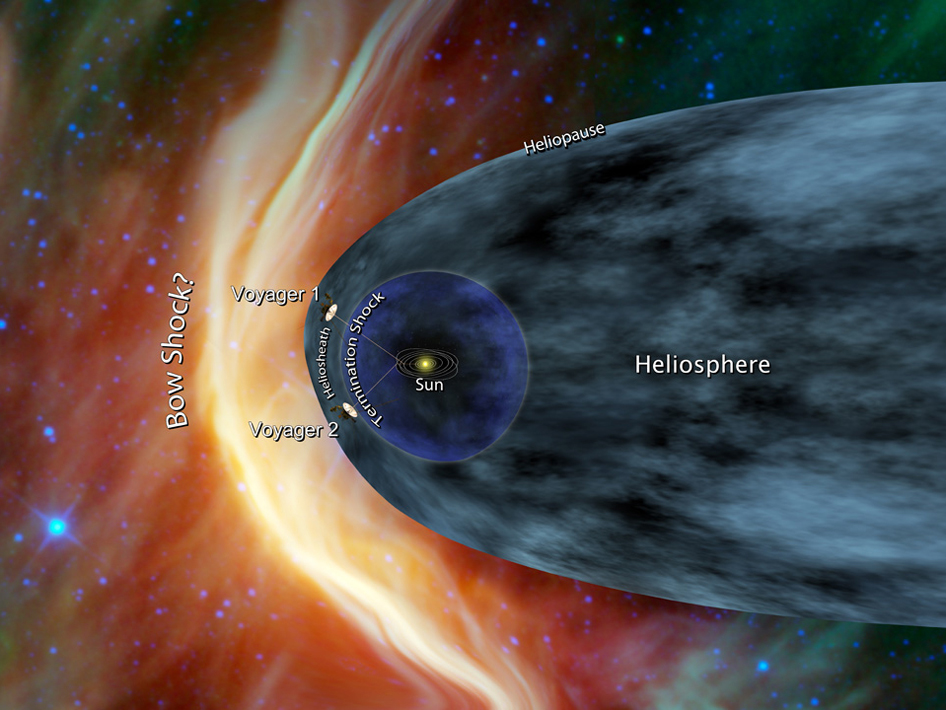
- Entering Interstellar Space
- Scientific Discoveries Made by Voyager 1
- Future Prospects for Voyager 1
- Comparison of Voyager 1's Speed with Other Spacecraft
- Challenges Faced by Voyager 1
- The Legacy of Voyager 1
How Fast is Voyager 1 Traveling?
Voyager 1 is traveling at an astonishing speed of approximately 38,000 miles per hour (61,000 kilometers per hour). This velocity allows the spacecraft to cover vast distances in space, moving further away from Earth with each passing day. To put this into perspective, Voyager 1 travels about 320 million miles (515 million kilometers) each year, steadily increasing its distance from the Sun.
The speed of Voyager 1 is primarily due to its initial launch velocity and subsequent gravitational assists from the outer planets. These gravitational boosts, particularly from Jupiter and Saturn, have enabled the spacecraft to achieve the incredible speeds necessary to escape the solar system.
Factors Influencing Voyager 1's Speed
- Initial Launch Velocity: The powerful rocket used to launch Voyager 1 provided the necessary thrust to escape Earth's gravity.
- Gravitational Assists: Encounters with Jupiter and Saturn significantly increased its speed through gravitational slingshot effects.
- Minimal Drag: In the vacuum of space, there is no air resistance to slow down the spacecraft, allowing it to maintain its speed over decades.
The Journey of Voyager 1
Launched in 1977, Voyager 1's primary mission was to explore the outer planets of our solar system. However, its journey has taken it far beyond that original goal. After completing its planetary studies, Voyager 1 continued on a trajectory that would eventually take it into interstellar space.
Key milestones in Voyager 1's journey include:
- 1979: Flyby of Jupiter, providing detailed images and data about the planet and its moons.
- 1980: Encounter with Saturn, studying its rings and moons, particularly Titan.
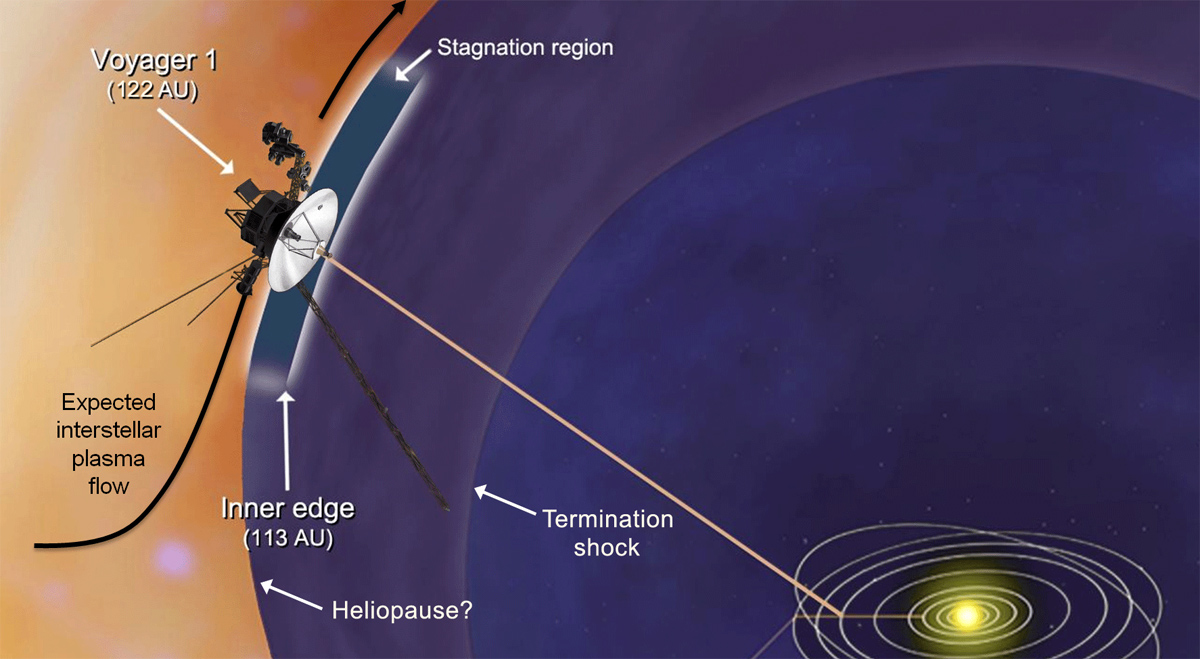
- 1998: Became the farthest human-made object from Earth.
- 2012: Entered interstellar space, crossing the heliopause boundary.
Today, Voyager 1 continues its journey, providing valuable data about the interstellar medium and the conditions beyond our solar system.
Technical Details of Voyager 1
Voyager 1 is equipped with advanced instruments and systems that have allowed it to function for over four decades. These include:
Read also:Exploring The Creative World Of Jeff Baena A Deep Dive Into His Career And Contributions
- Three Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generators (RTGs): These provide power to the spacecraft's systems and instruments.
- Scientific Instruments: A suite of instruments designed to study magnetic fields, plasma, cosmic rays, and other phenomena.
- Communication System: A high-gain antenna enables communication with Earth, despite the vast distance.
Despite the challenges posed by aging technology and diminishing power, Voyager 1 continues to operate and send back data to scientists on Earth.
Entering Interstellar Space
In 2012, Voyager 1 became the first human-made object to enter interstellar space. This milestone marked the crossing of the heliopause, the boundary where the Sun's influence ends, and interstellar space begins. The spacecraft's instruments detected significant changes in plasma density, confirming its transition into this new environment.
This achievement has provided scientists with unprecedented insights into the interstellar medium and the conditions beyond our solar system. Voyager 1's data has helped refine our understanding of the heliosphere and its interaction with the surrounding space.
Scientific Discoveries Made by Voyager 1
Throughout its journey, Voyager 1 has made numerous groundbreaking discoveries, including:
- Imaging of Jupiter's moons, revealing volcanic activity on Io and the icy surface of Europa.
- Study of Saturn's rings and moons, particularly Titan, providing insights into their composition and structure.
- Measurement of interstellar particles and magnetic fields, offering a glimpse into the environment beyond the solar system.
These discoveries have expanded our knowledge of the solar system and beyond, highlighting the importance of deep-space exploration.
Future Prospects for Voyager 1
While Voyager 1's power supply is gradually diminishing, it is expected to continue operating until around 2025. Beyond that point, its instruments will gradually shut down, but the spacecraft will continue its journey through interstellar space indefinitely.
Future missions inspired by Voyager 1's success may incorporate advanced technologies to explore even deeper into space. These missions could provide further insights into the interstellar medium and potentially discover new phenomena.
Comparison of Voyager 1's Speed with Other Spacecraft
Voyager 1 holds the record for the fastest human-made object traveling through space. However, its speed can be compared to other notable spacecraft:
- Parker Solar Probe: Currently the fastest spacecraft relative to the Sun, reaching speeds of up to 430,000 miles per hour (700,000 kilometers per hour).
- New Horizons: Known for its flyby of Pluto, it travels at approximately 33,000 miles per hour (53,000 kilometers per hour).
While Voyager 1 may not hold the title for the fastest spacecraft relative to the Sun, its sustained velocity and distance from Earth make it a remarkable achievement in space exploration.
Challenges Faced by Voyager 1
Despite its success, Voyager 1 has faced numerous challenges during its mission:
- Power Constraints: The spacecraft's RTGs gradually lose power, limiting the functionality of its instruments over time.
- Communication Delays: The vast distance between Voyager 1 and Earth results in significant communication delays, with signals taking over 20 hours to reach the spacecraft.
- Harsh Environment: The interstellar medium poses unique challenges, including exposure to cosmic rays and extreme temperatures.
Despite these challenges, Voyager 1 has continued to function and provide valuable data, demonstrating the resilience of its design and engineering.
The Legacy of Voyager 1
Voyager 1's legacy extends beyond its scientific achievements. It represents humanity's first step into interstellar space, symbolizing our desire to explore and understand the universe. The spacecraft carries a golden record containing sounds and images of Earth, serving as a message to any extraterrestrial life that may encounter it.
As Voyager 1 continues its journey, it inspires future generations of scientists and engineers to push the boundaries of space exploration. Its success highlights the importance of investing in long-term missions and the potential for groundbreaking discoveries.
Conclusion
Voyager 1's speed and journey through space exemplify humanity's achievements in deep-space exploration. By traveling at approximately 38,000 miles per hour and venturing into interstellar space, Voyager 1 has provided invaluable insights into the universe beyond our solar system. Its discoveries and challenges have paved the way for future missions and inspired countless individuals to pursue careers in science and engineering.
We encourage readers to share this article and explore other topics related to space exploration. Together, we can continue to expand our understanding of the universe and the possibilities it holds. For more information, consider visiting NASA's official website or other reputable sources to stay updated on the latest developments in space science.