Psoriasis on the foot is a chronic autoimmune condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing discomfort and impacting daily life. If you or someone you know is dealing with this condition, understanding its causes, symptoms, treatments, and lifestyle adjustments is essential for effective management. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to help you navigate through the complexities of foot psoriasis.
Psoriasis is more than just a skin condition; it is a complex disorder linked to the immune system. It can affect any part of the body, including the feet, and manifests in various forms. While there is no cure for psoriasis, understanding its nature and available treatment options can significantly improve quality of life.
In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and lifestyle tips for managing psoriasis on the foot. By the end of this guide, you will have a deeper understanding of how to address this condition and take proactive steps toward better foot health.
Read also:Exploring The World Of Hd Movie Hub 4u Your Gateway To Cinematic Excellence
Table of Contents
- What is Psoriasis on the Foot?
- Causes of Psoriasis on the Foot
- Symptoms of Psoriasis on the Foot
- Types of Foot Psoriasis
- Diagnosis of Psoriasis on the Foot
- Treatment Options for Psoriasis on the Foot
- Lifestyle Tips for Managing Psoriasis on the Foot
- Prevention and Management Strategies
- Living with Psoriasis on the Foot
- Conclusion and Call to Action
What is Psoriasis on the Foot?
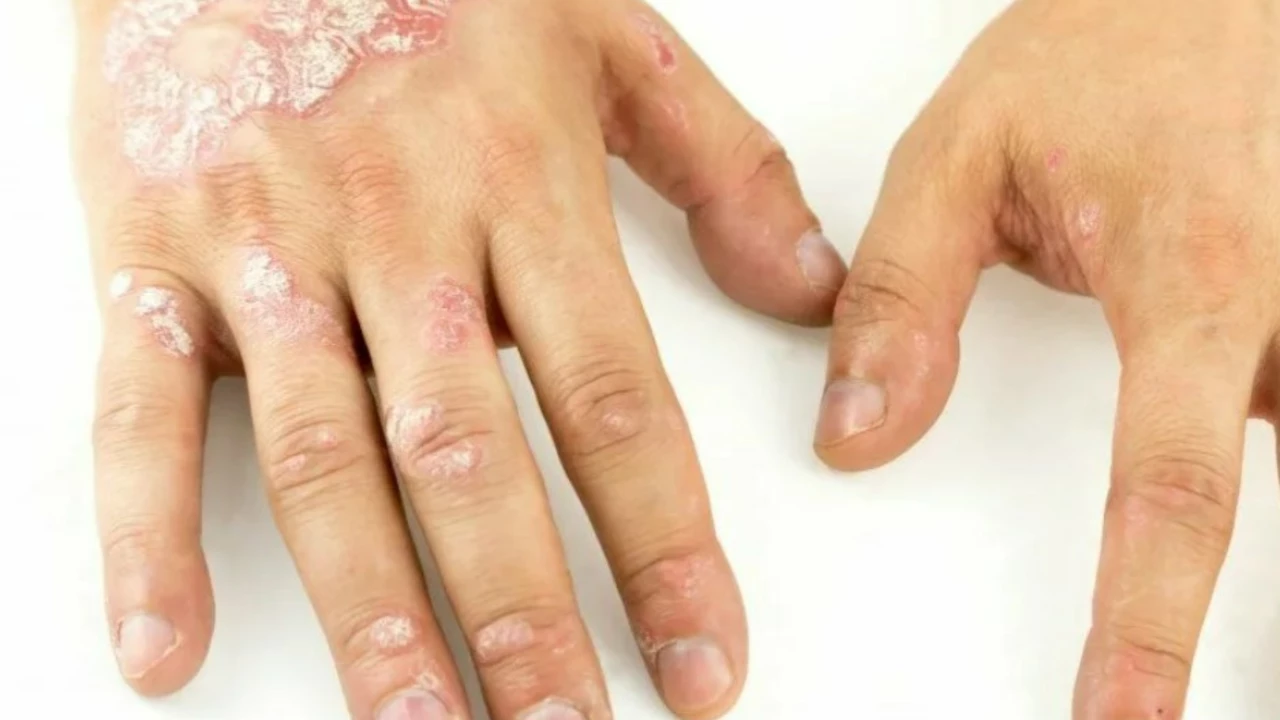
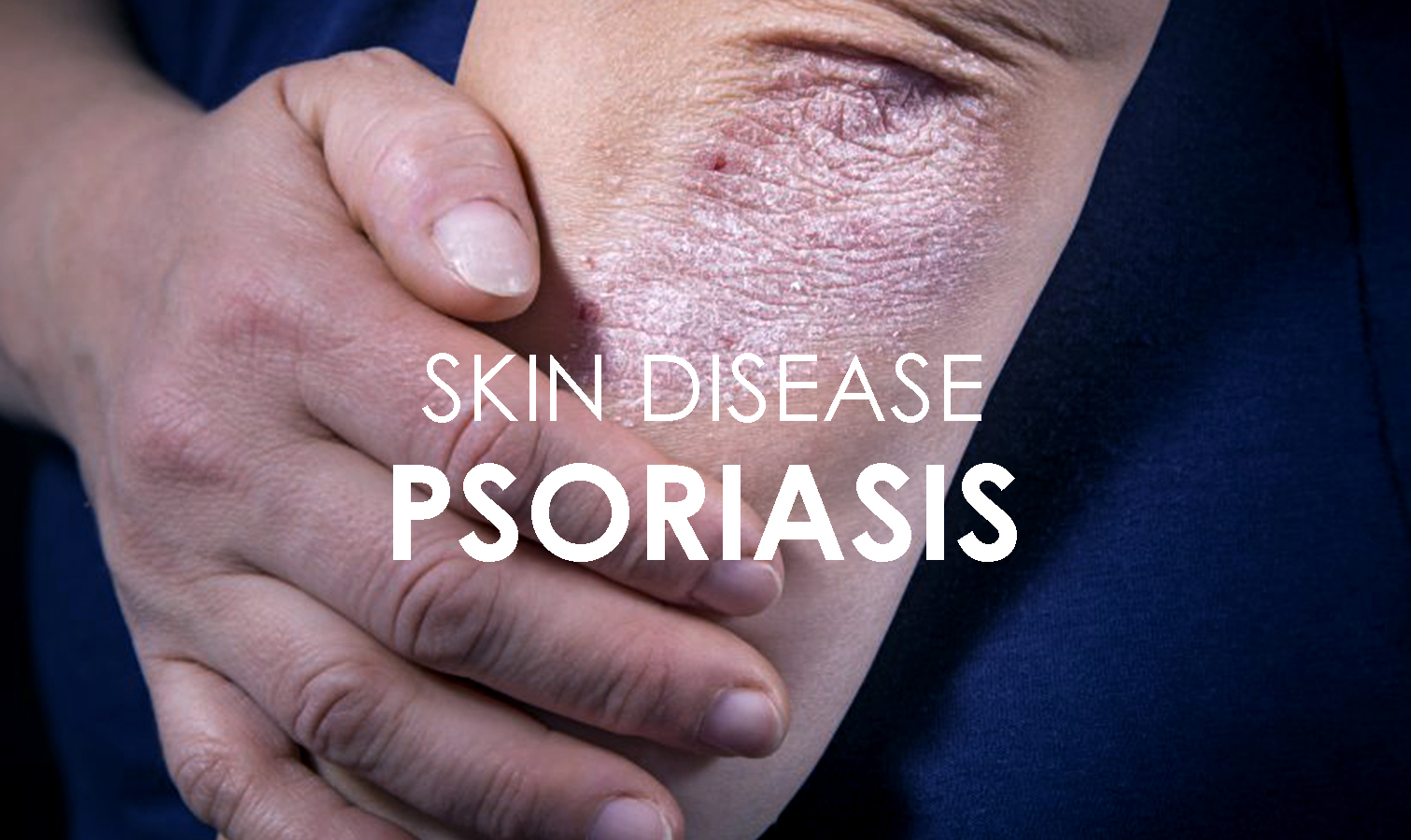
Psoriasis on the foot refers to a chronic autoimmune condition that primarily affects the skin of the feet. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly triggers an inflammatory response, leading to the rapid production of skin cells. This results in thick, scaly patches on the skin, often accompanied by itching, pain, and discomfort.
Understanding the Basics
Foot psoriasis is not contagious but can significantly impact daily activities such as walking, exercising, and wearing shoes. The condition can vary in severity, ranging from mild patches to widespread coverage of the feet. Early recognition and treatment are crucial for managing symptoms effectively.
Causes of Psoriasis on the Foot
The exact cause of psoriasis remains unclear, but research indicates that it is linked to genetic and environmental factors. Below are some of the primary causes of psoriasis on the foot:
- Genetic predisposition: Individuals with a family history of psoriasis are more likely to develop the condition.
- Immune system dysfunction: An overactive immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to inflammation and rapid cell growth.
- Triggers: Stress, infections, injuries, and certain medications can trigger psoriasis flare-ups.
Symptoms of Psoriasis on the Foot
Recognizing the symptoms of psoriasis on the foot is essential for timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Red, inflamed patches on the soles, heels, or toes.
- Thick, silvery scales covering the affected areas.
- Itching, burning, or soreness in the feet.
- Cracked skin that may bleed or cause discomfort.
- Thickened or discolored toenails.
Subtle Signs to Watch For
In some cases, psoriasis on the foot may present with less obvious symptoms, such as:
- Swelling or stiffness in the joints (a sign of psoriatic arthritis).
- Small pustules or blisters on the skin.
Types of Foot Psoriasis
There are several types of psoriasis that can affect the feet, each with distinct characteristics:
Read also:Who Is Joan Drummond Mcgowan Unveiling The Life And Legacy
Plaque Psoriasis
This is the most common type, characterized by raised, red patches covered with silvery scales. It often affects the soles of the feet and the heels.
Guttate Psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis appears as small, dot-like lesions and is often triggered by infections such as strep throat.
Pustular Psoriasis
This type involves white, pus-filled blisters surrounded by red, inflamed skin. It can be localized to the feet or palms.
Diagnosis of Psoriasis on the Foot
Diagnosing psoriasis on the foot typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare professional. In some cases, additional tests may be required:
- Skin biopsy: A small sample of skin is examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
- Ruling out other conditions: Conditions such as eczema or fungal infections may mimic psoriasis, so differential diagnosis is crucial.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis on the Foot
Treatment for psoriasis on the foot aims to reduce inflammation, slow down skin cell growth, and relieve symptoms. The following options are commonly used:
Topical Treatments
Creams, ointments, and medicated lotions containing corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, or salicylic acid are often prescribed for mild to moderate cases.
Phototherapy
Exposure to controlled doses of UV light can help reduce symptoms in moderate to severe cases. This treatment is typically administered under medical supervision.
Systemic Medications
For severe cases, oral or injected medications such as methotrexate, biologics, or immunosuppressants may be prescribed to control the immune system response.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Psoriasis on the Foot
In addition to medical treatments, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly improve psoriasis symptoms:
- Moisturize regularly: Use emollients to keep the skin hydrated and prevent cracking.
- Wear comfortable footwear: Choose shoes with adequate cushioning and support to reduce pressure on affected areas.
- Manage stress: Engage in relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
Prevention and Management Strategies
While psoriasis cannot be cured, proactive management can minimize flare-ups:
- Avoid known triggers such as smoking, alcohol, and certain medications.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Stay hydrated to keep the skin healthy and supple.
Living with Psoriasis on the Foot
Living with psoriasis on the foot can be challenging, but with the right approach, it is possible to lead a fulfilling life. Support groups, counseling, and open communication with healthcare providers can provide valuable resources and encouragement.
Emotional Well-being
Psoriasis can affect mental health, leading to anxiety, depression, or low self-esteem. Seeking professional help or joining a support network can be beneficial in managing these emotional challenges.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, understanding psoriasis on the foot involves recognizing its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. By adopting a proactive approach and following lifestyle tips, individuals can effectively manage this condition and improve their quality of life.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from the information. If you have any questions or personal experiences to share, please leave a comment below. For further reading, explore our other articles on skin health and wellness.
Data and references used in this article are sourced from reputable organizations such as the National Psoriasis Foundation and the American Academy of Dermatology, ensuring the reliability and accuracy of the information provided.