Understanding the Khalistan movement requires delving into its geographical boundaries and historical significance. The Khalistan movement has been a topic of global interest for decades, sparking debates about sovereignty, identity, and human rights. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the Khalistan map, its geographical context, and the historical events that shaped this region.
From the partition of India in 1947 to the ongoing discussions about an independent Khalistan, the region remains a focal point for scholars, historians, and policymakers. The struggle for Khalistan is not merely about borders but also about cultural and religious identity.
This article will explore the geographical boundaries of Khalistan, its historical background, and the socio-political implications of the movement. By understanding the map and context, readers can gain a deeper appreciation of the complexities surrounding this issue.
Read also:Hdhub4ucom Your Ultimate Destination For Highquality Movies And Entertainment
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Geography of Khalistan
- Historical Context
- The Partition of India
- The Khalistan Movement
- Khalistan Map
- Religious and Cultural Significance
- Political Implications
- International Perspective
- Future of Khalistan
- Conclusion
Introduction
The concept of Khalistan has its roots in the history and geography of Punjab, a region rich in cultural heritage and religious significance. The term "Khalistan" refers to the proposed sovereign state for the Sikh community, primarily located in the Punjab region of India. Understanding Khalistan involves examining its geographical boundaries and the historical events that have shaped the movement.
Punjab, often referred to as the "breadbasket of India," is a fertile region with a rich agricultural tradition. The geographical features of the region play a crucial role in its economic and cultural significance. Historically, Punjab has been a melting pot of cultures, influenced by various empires and civilizations.
The Khalistan movement emerged in the late 20th century as a response to perceived injustices and marginalization faced by the Sikh community. The movement gained momentum in the 1980s, leading to significant political and social upheaval in India.
Geography of Khalistan
The proposed Khalistan map includes the Punjab region, which spans parts of India and Pakistan. The geography of Khalistan is characterized by the fertile plains of the Indus River basin, making it one of the most productive agricultural regions in the world.
Key Geographical Features
- Rivers: The Indus, Ravi, Beas, Chenab, and Sutlej rivers are vital to the region's agriculture and economy.
- Climate: Punjab experiences a temperate climate with distinct seasons, including hot summers and cold winters.
- Topography: The region is predominantly flat, with some hilly areas in the northern parts.
According to the United Nations, the Punjab region is one of the most densely populated areas in South Asia, with a diverse population of Hindus, Muslims, Sikhs, and other religious groups.
Historical Context
To understand the Khalistan movement, one must explore the historical context of the Punjab region. The history of Punjab is marked by the rise and fall of various empires, including the Mauryas, Kushans, and Mughals. The Sikh Empire, established by Maharaja Ranjit Singh in the early 19th century, played a pivotal role in shaping the region's identity.
Read also:Haiden Deegan Dad A Comprehensive Look Into The Life And Legacy Of A Motocross Legend
Key Historical Events
- 1799-1839: Establishment of the Sikh Empire under Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
- 1849: Annexation of Punjab by the British Empire.
- 1947: Partition of India and the division of Punjab between India and Pakistan.
These events laid the foundation for the modern-day Khalistan movement, as the Sikh community sought to preserve its cultural and religious identity in the face of political changes.
The Partition of India
The partition of India in 1947 had a profound impact on the Punjab region, dividing it between India and Pakistan. The partition led to one of the largest mass migrations in history, with millions of Hindus, Muslims, and Sikhs crossing the newly drawn borders.
Consequences of Partition
- Violence: Communal riots resulted in the loss of countless lives and displacement of communities.
- Economic Impact: The division of Punjab disrupted agricultural and industrial activities, affecting the region's economy.
- Cultural Loss: The partition led to the fragmentation of cultural and religious communities, creating lasting tensions.
Scholars such as Ian Talbot and Joyce Pettigrew have extensively studied the partition's impact on Punjab, highlighting the human cost and long-term consequences.
The Khalistan Movement
The Khalistan movement emerged in the 1970s as a response to perceived injustices faced by the Sikh community in India. The movement gained momentum in the 1980s, leading to significant political and social unrest.
Key Figures and Events
- 1984: Operation Blue Star, a military operation conducted by the Indian government, led to the storming of the Golden Temple in Amritsar.
- Assassination of Indira Gandhi: The assassination of the Indian Prime Minister by her Sikh bodyguards further escalated tensions.
- 1990s: Decline of the movement due to government crackdowns and internal divisions.
Despite its decline, the Khalistan movement continues to resonate with some sections of the Sikh diaspora, particularly in countries like Canada and the United Kingdom.
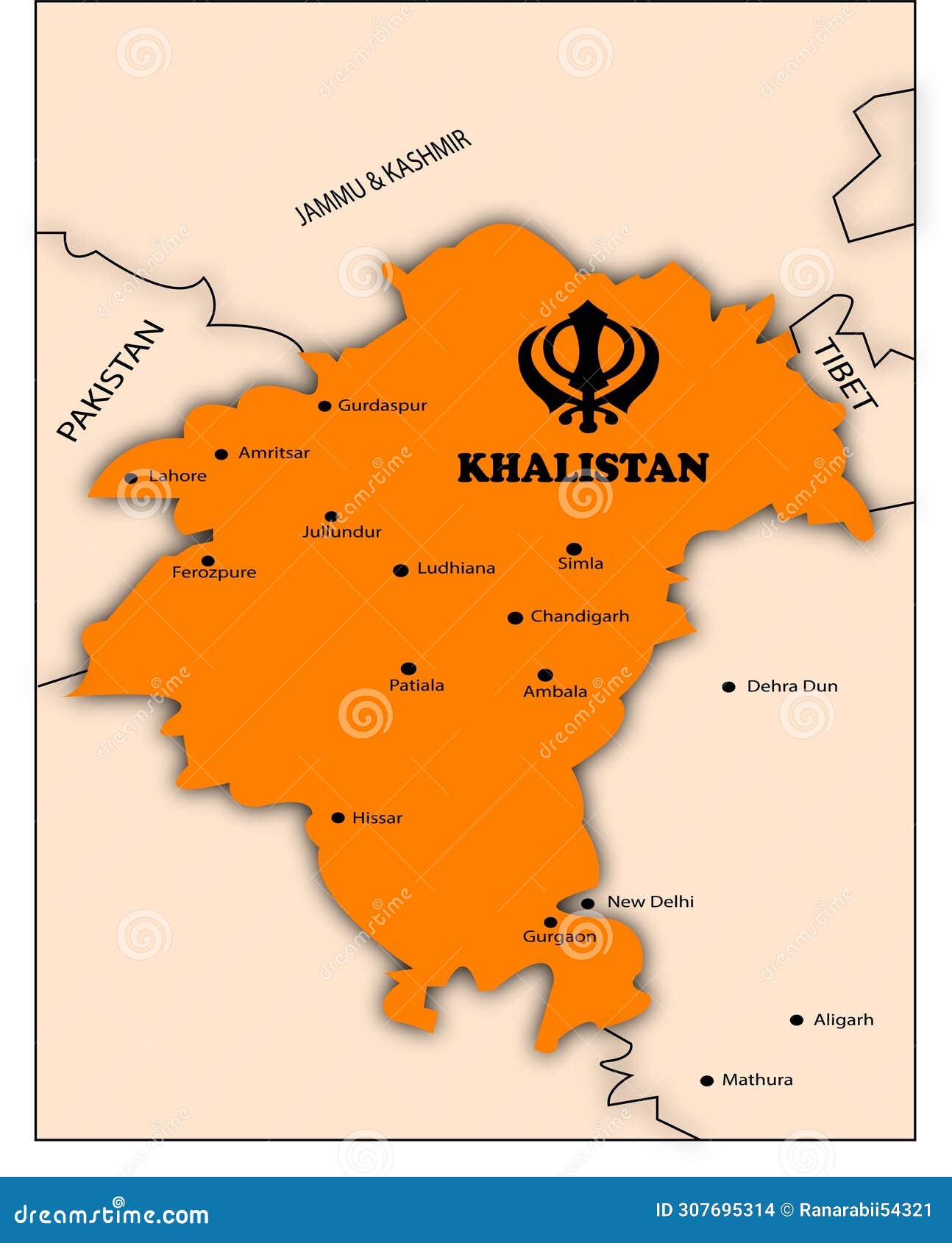
Khalistan Map
The proposed Khalistan map includes the Punjab region of India and parts of Pakistan. The map outlines the geographical boundaries of the proposed state, highlighting key cities and landmarks.
Key Cities in the Proposed Khalistan Map
- Amritsar: Home to the Golden Temple, the holiest site in Sikhism.
- Ludhiana: A major industrial hub in Punjab.
- Jalandhar: Known for its sports goods industry and cultural significance.
According to the Indian Ministry of Home Affairs, the proposed Khalistan map represents a significant challenge to India's territorial integrity and national security.
Religious and Cultural Significance
The Khalistan movement is deeply rooted in the religious and cultural identity of the Sikh community. Sikhism, founded by Guru Nanak in the 15th century, emphasizes equality, justice, and devotion to God.
Key Religious Sites
- Golden Temple (Harmandir Sahib): The most sacred site in Sikhism, located in Amritsar.
- Takhts: Five revered seats of authority in Sikhism, including the Akal Takht in Amritsar.
- Gurdwaras: Places of worship and community centers for Sikhs.
The cultural significance of Punjab extends beyond religion, encompassing music, dance, and literature. The Bhangra dance and Punjabi poetry are celebrated globally as symbols of Punjabi culture.
Political Implications
The Khalistan movement has significant political implications for India and the international community. The movement challenges the notion of a unified India and raises questions about minority rights and self-determination.
Government Response
- Anti-Terrorism Laws: The Indian government enacted stringent laws to combat Khalistani militancy in the 1980s.
- Dialogue: Efforts to engage with moderate Sikh leaders have yielded mixed results.
- International Pressure: India has sought to isolate Khalistani groups abroad by lobbying foreign governments.
Political analysts such as Sumit Ganguly argue that addressing the root causes of the movement requires a comprehensive approach, including political reforms and economic development.
International Perspective
The Khalistan movement has garnered international attention, particularly among the Sikh diaspora. Countries like Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States have witnessed protests and rallies in support of Khalistan.
Global Response
- Canada: Home to a large Sikh population, Canada has faced pressure to address Khalistani activities on its soil.
- United Kingdom: The UK government has condemned Khalistani extremism while engaging with moderate Sikh groups.
- United States: The US has labeled some Khalistani groups as terrorist organizations, aligning with India's stance.
International organizations such as Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch have called for a balanced approach, emphasizing the need to protect human rights while addressing security concerns.
Future of Khalistan
The future of Khalistan remains uncertain, as the movement continues to evolve in response to changing political and social dynamics. While the intensity of the movement has waned in recent years, it remains a potent symbol of Sikh identity and aspirations.
Challenges and Opportunities
- Economic Development: Investing in Punjab's infrastructure and agriculture could address some of the grievances fueling the movement.
- Political Reforms: Strengthening democratic institutions and ensuring minority rights could help build trust between the Sikh community and the Indian state.
- Global Engagement: Engaging with the Sikh diaspora and addressing their concerns could foster greater understanding and cooperation.
Experts such as Paul Brass suggest that a peaceful resolution to the Khalistan issue requires dialogue, empathy, and a willingness to address historical injustices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the Khalistan movement involves examining its geographical boundaries, historical context, and socio-political implications. The proposed Khalistan map represents more than just a territorial claim; it symbolizes the aspirations and identity of the Sikh community. By addressing the root causes of the movement and fostering dialogue, there is hope for a peaceful resolution.
We invite readers to share their thoughts and insights in the comments section below. For more information on related topics, explore our other articles on global politics and history. Together, we can promote understanding and foster a more inclusive world.

![Understanding the Khalistan Map [2023] FAIR](https://fairbd.net/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Khalistan_Map_Sikh_For_Justice.webp)