Wolves have long been associated with their hunting prowess, but do wolves scavenge? The question is more complex than it seems. Wolves are apex predators, but their feeding habits go beyond hunting alone. Understanding their behavior and diet can provide valuable insights into their role in ecosystems and their adaptability to changing environments.
For centuries, wolves have been the subject of fascination and fear. While many people associate wolves with hunting, their dietary habits are more nuanced. They are opportunistic feeders, meaning they take advantage of available food sources, including scavenging when necessary. This adaptability has allowed them to survive in diverse habitats around the world.
This article delves deep into the question of whether wolves scavenge and explores the truth behind their feeding habits. By examining scientific studies, expert opinions, and real-world observations, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of how wolves interact with their environment and what drives their dietary choices.
Read also:Who Is Joan Drummond Mcgowan Unveiling The Life And Legacy
Table of Contents:
- Biography of Wolves
- Wolf Feeding Habits
- Do Wolves Scavenge?
- Diet Composition
- Role in Ecosystems
- Adaptability in Feeding
- Common Myths About Wolves
- Conservation Efforts
- Scientific Research on Wolves
- Conclusion
Biography of Wolves
Wolves (Canis lupus) are highly social animals that belong to the Canidae family. They are native to the Northern Hemisphere and are known for their intelligence, strength, and cooperative behavior. Wolves play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by regulating prey populations.
Key Facts About Wolves
Below is a summary of key facts about wolves:
| Scientific Name | Canis lupus |
|---|---|
| Habitat | Tundra, forests, grasslands, deserts |
| Diet | Carnivorous (primarily large ungulates) |
| Social Structure | Pack-based hierarchy |
| Conservation Status | Varies by region (some populations are endangered) |
Wolf Feeding Habits
Wolf feeding habits are a fascinating area of study. While they are primarily hunters, their diet is influenced by factors such as prey availability, seasonal changes, and competition with other predators. Understanding these habits provides insight into their role as both hunters and scavengers.
Primary Food Sources
- Large ungulates like deer, elk, and moose
- Smaller mammals such as rabbits and rodents
- Occasionally fish and berries in certain regions
Studies have shown that wolves rely heavily on large ungulates for sustenance, but they are not averse to other food sources when needed.
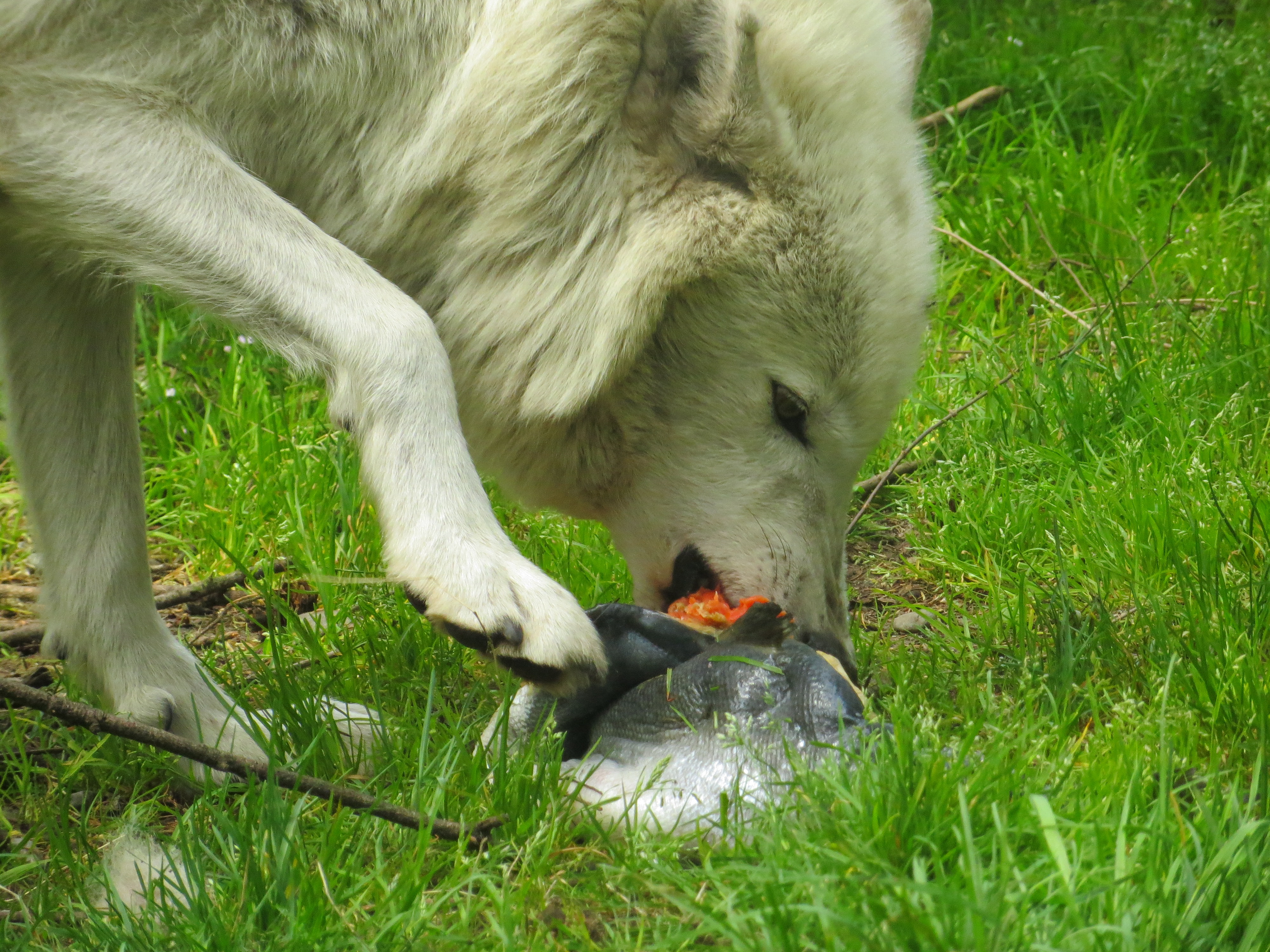
Do Wolves Scavenge?
The question of whether wolves scavenge is central to understanding their feeding habits. While wolves are skilled hunters, they are also opportunistic feeders. Scavenging is a natural behavior that allows them to survive during periods when hunting is less successful.
Read also:David Muir In Relationship Exploring The Life Career And Love Story Of The Renowned Journalist
Research published in the Journal of Wildlife Management indicates that wolves may scavenge up to 20% of their diet, depending on environmental conditions. This behavior is more common in winter when prey is scarce or when carcasses left by other predators are available.
Diet Composition
The diet of wolves is diverse and varies depending on their location. In general, their diet consists of:
- 70-90% meat from hunted prey
- 10-20% scavenged food
- Occasional plant material, especially in summer
Scientists emphasize that wolves are not strictly carnivorous and may consume plant matter to supplement their diet, particularly during lean times.
Role in Ecosystems
Wolves play a vital role in maintaining healthy ecosystems. By regulating prey populations, they prevent overgrazing and promote biodiversity. Their scavenging behavior also contributes to nutrient cycling by breaking down carcasses and returning nutrients to the soil.
Effects on Prey Populations
Studies conducted in Yellowstone National Park demonstrate the positive impact of wolves on ecosystems. Since their reintroduction in 1995, wolves have helped restore balance by controlling elk populations, which in turn has allowed vegetation to recover.
Adaptability in Feeding
One of the most remarkable traits of wolves is their adaptability. They can thrive in a wide range of environments, from Arctic tundra to desert landscapes. This adaptability extends to their feeding habits, allowing them to survive in challenging conditions.
For example, in areas where large prey is scarce, wolves may rely more heavily on scavenging or smaller prey. This flexibility ensures their survival even when faced with environmental changes or human activity.
Common Myths About Wolves
There are many misconceptions about wolves, especially regarding their feeding habits. Below are some common myths and the truth behind them:
- Myth: Wolves only hunt and never scavenge.
Truth: Wolves are opportunistic feeders and will scavenge when necessary. - Myth: Wolves always hunt in large packs.
Truth: While wolves often hunt in packs, solitary wolves or smaller groups can also be successful hunters. - Myth: Wolves kill for sport.
Truth: Wolves hunt to survive and rarely kill more than they need.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts are critical to ensuring the survival of wolf populations worldwide. Habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, and illegal hunting remain significant threats to wolves. Organizations like the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and the International Wolf Center are working to protect wolves and their habitats.
Public education and community involvement are essential components of conservation efforts. By promoting coexistence between humans and wolves, we can help preserve these magnificent creatures for future generations.
Scientific Research on Wolves
Scientific research continues to uncover new insights into wolf behavior and ecology. Advances in technology, such as GPS collars and remote cameras, have allowed researchers to study wolves in unprecedented detail.
A study published in Science highlights the importance of wolves in maintaining ecosystem health. The research emphasizes that preserving wolf populations is essential for biodiversity and ecological balance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wolves are complex and adaptable creatures with diverse feeding habits. While they are skilled hunters, they also scavenge when necessary, demonstrating their ability to thrive in various environments. Understanding their role in ecosystems and addressing conservation challenges are crucial steps toward ensuring their survival.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. For more articles on wildlife and conservation, explore our website and stay informed about the latest developments in the field. Together, we can make a difference in protecting these incredible animals and their habitats.